TPT Notes
Week 32 - 5/19 Notes
Graph Theory
- Vertice - point on the graph
- Edge - line that connects two vertices
- Create a graph and make different points
- DepthFirst search - input vertix, finds point from
for loopin array of vertices- checks if there are attached vertices
- marks next vertice we will visit
- start from
a–>b–>f–>a–>c d–>b–>a–>cf–>b–>a–>c–>b–>d–>e- real world example: plane flight routes
- readFirst search
- data structures in nodes
Week 29 - 4/3 Notes
Hashmaps
- Uses a hash function to map key functions
- does not maintain insertion order either by key or by the order inserted
- methods include:
get()andput() - allows any non-null object as a key
Hacks
- Analyze the Big O complexity on Sorts.
- Establish analytics including:time to sort, number of comparisons and number of swaps.
- Average the results for each each Sort, run each at least 12 times and 5000 elements.
- You should throw out High and Low when doing analysis.
- Make your final/judgement on best sort: Number of Comparisons, Number of Swaps, Big O complexity, and Total Time.
- Build your own Hashmap. Make a HashMap to correspond to a Data Structure using a Collection.
- Be sure to have 5000 records
- Perform analysis on Binary Search vs HashMap Lookup, try using random to search and find 100 keys in 5000 records. Perform 12 times and throw out high and low.
- Extra, Practical learning
- Performing Iteration, Delete, and Add operations are another way to analyze Collection vs HashMap data structure.
- A HashMap and a Collection can be used in a Class, POJO and API.
- Make a Diagram on the Pros and Cons of Collection vs HashMap
Week 28 - 3/27 Notes
Sorting
- renamed type to
Collectable - implements from Java
- some methods are:
filter(),map(),reduce(), andcollect()
- some methods are:
- implement a
compareTo()–> find an object- sort algorithms build into
LinkedListdata structures
- sort algorithms build into
...- takes multiple lists
Week 27 - 3/20 Notes
Sorting
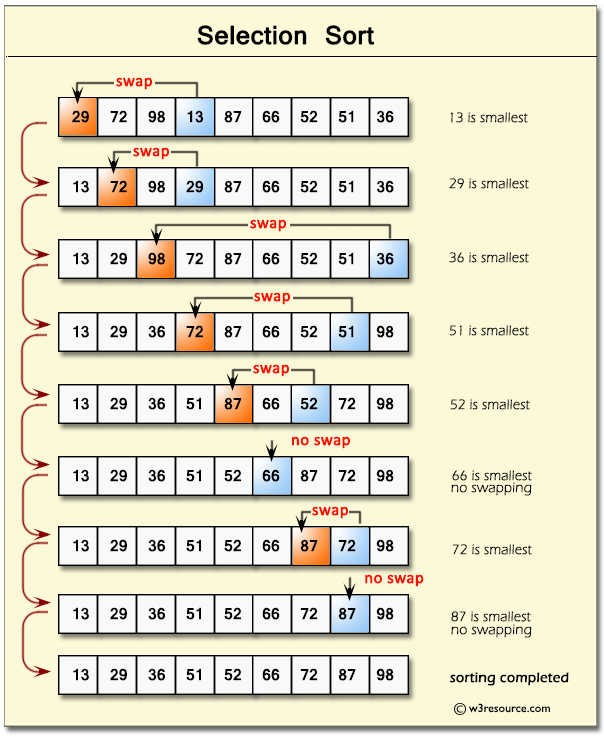
- Selection Sort - a linear sort algorithm as it moves from index
[0]to[n-1]. In the inner loop which is a second linear loop it compares two elements (like seen in the visual below) and notes which is smallest, after cycling to the end it swaps the smallest number to beginning position in the round.
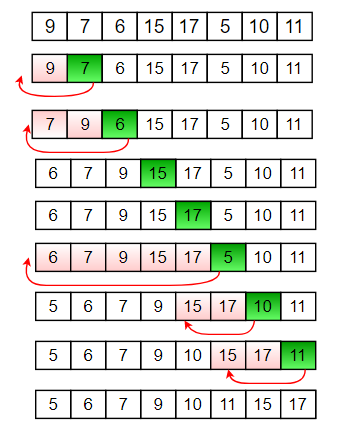
- Insertion Sort - another linear algorithm that sorts elements from index
[0]to index[n-1]. In the inner loop of this algorithm, it finds the gap, insertion point for the next item and inserts it. Each inner loop leave the list partially sorted according to outer loops index.
- Merge Sort - uses a divide and conquer algorithm, versus linear algorithm of insertion or selection sort. Looking at it can be complicated, but it is more simple than it looks. It divides the array into two different groups recursively, until it gets only two to compare, swaps if necessary. Then it pops out of the recursion, observe the cascading and then the inverted assembly in illustration, after pop it puts each split group back together using a sorted comparison.

- Bubble Sort - works by repeatedly swapping the adjacent elements if they are in the wrong order. This algorithm is not suitable for large data sets as its average and worst-case time complexity is quite high.
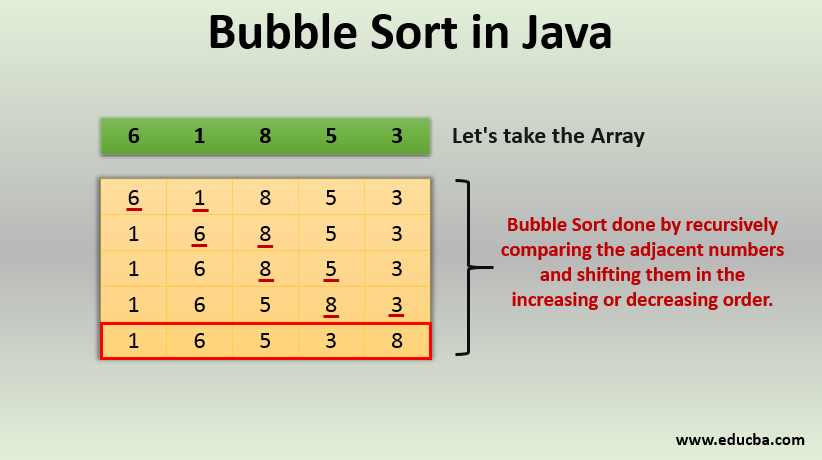
Hacks
- Build into this Jupyter Notebook(s) for Bubble Sort, Selection Sort, Insertion Sort and Merge Sort.
- Build into this Jupyter Notebooks Tester methods that runs each Sort
- Commit to GitHub Repository often, try to use GitHub commits to show iterations on work
- Note, build your sorts into Generic T Queue using toString and compareTo to compare keys.
Week 26 - 3/13 Notes
Arrays, ArrayLists, and 2D Arrays
- 2 reference data types
- Objects
- Arrays
Collection Framework
- Overriding allows a subclass or a child class to provide a specific implementation of a method that is already provided by one of its super-classes/parent classes
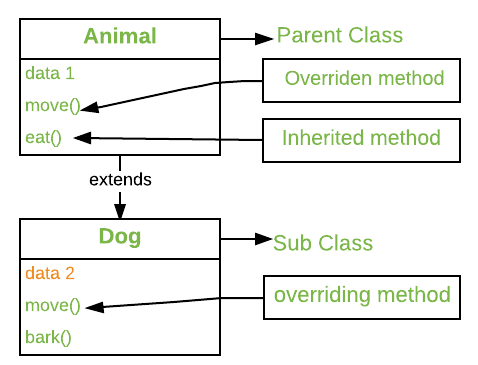
- Static methods can be called without creating an object of the class
- EX:
public static void main(String[] Args)
- EX:
- Instance methods are part of the object of the class
- They need an object to be created in order to be called
Week 25 - 3/6 Notes
Data Types, Methods, Control Structures
- Goals for tri - prepare for AP test & create a project for Mr. M
- When we return from spring break - 2 weeks until AP exam
- Midterm Project - teaching 15-25 min lesson (w/ hacks)
- focusing on FRQ types
- must be unique
- Prepare ahead for tech-talk!!
To-Do
- Monday: Form teams and work, review Tech Talk. Start quiz.
- Tuesday: Early Seed award check. Tech Talk on Data Types
- Wednesday: Plan and work out key objectives ‘till Midterm Final’, you should plan Individual and Team criteria.
- Thursday: Work Day. Data Types, Plans, Quiz
- Friday: Work Day
Data Types Notes (Tech Talk)
- Before tech-talk:
- Write a sample binary addition 1 + 1 = 10
- Have Java Code cell on screen at start of lecture
- Data types for AP Exam
- int
- float
- double
- char
- boolean
- objects (reference)
- arrays (reference)
- Other data types
- long
- short
- byte
- Primitive data types - basic building blocks of data that holds a single data type
- they are not objects
- stored directly in memory and are passed by value
- Reference data types - object is passed as a parameter to a method, and the object is passed as a class
- pointer -
. - EX:
n.hashcode()
- pointer -
intVSIntegerint- data type that stores 32-bit signed two’s complement integer
- a primitive data type
- helps store integer values in memory
Integer- class that wraps a primitive type int in an object
- a wrapper class
- helps to convert in into objects and to convert an object into int
- Complex data types
- Array VS Class
- class has methods and data, which can have different data types
- arrays must be the same data type
- Array VS Class
Week 18 - 1/9 Notes
View and Frontend Coding
- GitHub pages that show what your are doing, but not yet implemented
- Think about what you are going to design, before you implement features
- Make a site theme
layouts/default.htmlimports SASS locally- has menu across top
- Observing what happens in
_site - CRUD concepts
html 5- if you type something that is incorrect, there will be multiple errors
Week 17 - 1/3 Notes
Creative, Collaborative, and Quality Culture
- What would you code given absolute freedom?
- I want to code a to-do/reminders list or a game involving machine learning
- What would motivate you to be productive each day given the freedom to code what you want?
- I want to have a to-do list that works the best for me. I think that if I design my own to-do list, I can use it more. I have always found machine learning to be really interesting and it’s something that I want to learn and improve on.
- In a project, most students are more motivated if the project seems useful, unique, and has an interested consumer. How will you maintain motivation?
- I will try to find something that my group is really interested in and passionate about. It should also be something that others might also have interes in. I can also talk with my group and see what ideas we have for our project. We can build off different ideas and see what each person is interested in.
- Provide summary in comment on why information is this blog is important?
- I think it’s important to colaborate and make sure everyone in the group is on the same page. It’s important to track team progress and see who is behind. I want my team to be comfortable together and help each other with problems that others do not understant
- Would you rather work on PBL project, or or do assigned free-response coding questions (aka FRQs)? Which would be easier to meet class standards?
- I would rather do assigned FRQs because in PBL projects I feel like I have never fully understood the concept we are learning. I often feel overwhelmed by the amount of topics we learn in PBL and it’s easier for me to focus on just a few topics. In FRQs, there is just one topic we focus on and there are multiple parts to that FRQ that use the topic in different ways. I feel like PBL is great for colaboration, but FRQs can also implement colaboration within them. I liked the FRQs we did before break because we had the freedom to add something to make the FRQ unique.
- Trust and Freedom are often earned. How will you show your passion and ability to succeed in your work?
- I will show what I know by making sure I measure my progess each deay in my review ticket. I often feel like I am constantly spending a lot of time on my work, even though I don’t make a lot of progress. I constantly undo and redo parts and it’s very time consuming for me. Tracking my progress each day will allow me to see what I have accomplished
- What key learnings and focusses are a priority for you?
- I want to improve my ability on backend development. I feel like I focus too much on the frontend and the styling.
Extra Credit Reflections
- Don’t write bullet points - take advice personally
- Write about things that inspire you
Week 15 - 12/5 Notes
- 2D Array is an array of arrays
- Kind of like a grid, have as many as columns and rows
- Declaring a 2D Array:
int[][] numbers;String[][] names;
- to initialize a 2D array, you have to iterate through each row and each column
- have a nested for loop
- Display values backwards/upside down
FRQ 4 - 2D Arrays
- Hacks:
- Create API
- Look through actual FRQ 4
- due: 12/12 @11:59
Week 114 - 11/28 Notes
- Palm files
- palm.xml: versions of dependency should be left out
- System will automatically fill in version
- Debugging: post in postman, git in postman
- executing code from Spring Portfolio
- Ask yourself question: “Why am I doing this?”
Unit 7 - ArrayLists
- A reference type
- Change size dynamically
- methods:
add(int index, element)size()clear()remove()get(int index)
- Enhanced for loops
- iterate through every element in a list
- Searching - locating data within linear structures (arrays, lists, queue, stack, etc.)
- For loops are very important for linear searching because it needs to be specified sequentially
- No need to track index after execution
- Order matters in seaching
- 5 rubber ducks with an individual number (green, pink, pink, blue, green)
- Removing 1 pink duck - move through each duck to see if its pink
- Sort in ascending and descending order
Week 13 - 11/14 Notes
- 4 types of FRQs
- Spring, APIs, and JPAs are easy to use with Java
- Learn why people love Java
- Should memorize 10 units and 4 FRQ types
- FRQ #1 due FRIDAY, FRQ #2 due MONDAY AFTER BREAK
- Show some sort of testing using screenshots
- Required for team project
- Build off of previous projects
- Avoid starting from scratch
- See if teacher likes it
- Find something with use
- Be interested in it
- Talk with team
.toString–> must be pre-defined-
Everything in Java is passed by reference
- 4 Types of FRQs
- Methods and Control Structures - 2
- Classes - 5
- Array/ArrayList - 6/7
- 2D Array - 8
Degugging
- click the debug button on VS Code instead of run
FRQ 1 - Methods and Control Structures
FRQ 2 - Classes
- POJO
- Add name, birthday, and email
- Hacks:
- Tester method on POJO
- fix bug - overrides and sets a new DOB
- We need to add data, not replace it
- New method to add data
TRI 1
Class Lessions
Definition Signature Method Body
camelCase - start with lowercase, then every word is uppercase to separate word
return void - returns nothing, code just executes
- static –> do not require an object to access the methods in the class
-
non-static –> requires an object to acces methods in class
-
.this - private
- public
- protected
public static void main (String[] Args) –> what you need for a method
- Accessor: methods access to variable methods return statement
-
Autator: classes ability to change value of variable
- Local: only call within method
- Global: all methods can access variable
Primitives
- Why Java?
- More flexible OOP
- Run an any platform
- Garbage collection –> memory management, when a variable is no longer used it’s
- Multi-threading: able to acces different
- Primitives
- Predefined
- lovercase
- ex: boolean, int, double, char, long, short
- Non-Primitives
- Strings
- capital
- How to name
- letters, numbers, or underscores
finalmakes variable constant- Casting –> changing data types
- int to a double
- Narrowing is going from bigger data to smaller
- Operators
- +, -, *, /, %, ++, –, +=, -=, *=, /=, %=
- Mod returns the remainder
- overflow errors –> left to right (PEMDAS)
- Incremet and decrement operators –> adds 1 and subract 1
- Coding Challenge
- Scanner
- import
Scannerclass
- import
Week 8 - 10/11 Notes
- Project planning for website
- Requirements
- Explain process –> succuss/failures
- When program is ran, should have some sort output
- Minimul amount of code as possible
- extends
- re-using code
- Coding is never done ;)
Week 7 - 10/4 Notes
- Fetch –> JavaScript
- Different ways to process an API
- Every attribute –> 1 setter and 1 getter
- 4 attributes –> constructor has 4 attributes
- Postman: git –> put –> tool for backend
ArrayLists
- Uses generic data types
- Defined in
< > - Enter any object into “
ArrayList”
Extends/Implements
- Use extends as an alternate way to copy/paste
Jokes
- Deployment:
- AWS
- POJO (Plain Old Java Object)
- Simple –> ex: class, methods(functions), and attributes(varibles/arguments)
- Setters –> set values to attributes
- Constructors are automattically made
- Zero argument constructor –>
public ClassName() - All argument constructor:
public ClassName()
{
this.attributes = attributes;
} - Code first database –> build an entity with and SQL database
- CRUD (Create Read Update Delete)
init()–> runs independently
TO-DO
- ArrayLists
- Frontend/Backend
- Integration w/ crossover team about project
- Create a poster for the classroom
- Work on College Board Presentations (Arrays)
Week 6 - 9/27 Notes
- Points:
- Friday –> closing gradebook, fix issues w/ points by Friday
- Images for Java
- Rapid API
- Review for project
-
Interest by each individual
- Make abstract class: define init() for extending
- you do not inherit constructors
- must use
super()
- must use
- Telescoping - one constructor goes into another constructor
- polymorphic behavior –> two methods that the same name, but one has it’s own instances, and the other does not
- Override –> doesn’t need but prefer to see
- User can see clearly that the class is extended
- Protected –> only inherited classes can access
- Public –> can access it in other classes
-
Private –> cannot access outside class
- Minimize lines of code >:)))
- For loop with arrays:
- each element is assigned to 2 values (0 & 1)
- decrement operator:
-- - change
super()name
Week 5 - 9/20 Notes
- Try to abstract init()
- @Override init()
- Hacks –> while loop, recursion, see comments in code
JavaScript Tutorial
- Goal this week: Design
- JavaScript VS Java –> marketing
- Syntax is a little similar to Java
- JSON
Program Design
- Data & Visual
- Pick something that everyone in the group is interested in
- Have code base –> brainstorm what you are going to use
- UML, how to separate things to-do into parts for each person to do
- Think about key technical algorithmic problems
- Testing –> debugging, unit testing, main method
- Without testing methods, code will break
Teacher Ideas
- redo college board
- Redo it for different AP classes
- Way for you to study
- Classroom management
- Databases
- Finding GitHub usernames and repos
Project Plan
- Find project plan by next week
- Frontend & Backend
- Visuals
- Java
- Add arrays + arrayLists
Week 4 - 9/13 Notes
Iteration with 2D Arrays
- Recreate monkey program
- Tic-Tac-Toe
Java Spring/Thymeleaf
- cache - the process of storing things locally
- Deployment –> put server into
- Default for Java: 80:80
- Changed to prevent clashing
- Changed to 80:85
- CODE CODE CODE:
- Spending too much money on Amazon :((
- Delete all of instances on AWS
- Make 1 instance per team
- 8G –> whole team won’t fit
- Figure out how to pick a port
- Use 80:85
- Index is automatically named by Java
- Greet –> type in name and computer says hello
Human Day 2
- Agile - grows and develops
- Avoids methodology
- Adapt to certain problems
- Use a SCRUM board
- Live review –> product demo
- Extreme programming
- Pair-programming
- Test Driven Development - test towards criteria
- Small details or broad details
Week 3 - 9/7 Notes
Boolean Expressions and If Statements
- Boolean - logical statement that can be evaluated to the values true/false
- EX:
if (true) { System.out.println("True code block"); } - LOGICAL OPERATORS
- && - and
-
- or - ! - not
- Parenthesis matter
- De Morgan’s Law
- (A ∪ B)’ = A’ ∩ B’
- “The complement of the union of the two sets A and B will be equal to the intersection of A’ (complement of A) and B’ (complement of B).”
- EX:
!((false || !true) || (false && true))
PBL Tip: have the least amount of logical operators as possible
- Hacks:
- Build your own Jupyter Notebook lesson on ifs
- Explain if, if-else, and if-elseif-else.
- Make a markdown block before you sample code
- Comment in code to describe each decision
- Add to lesson switch-case
- Create and if-elseif-elseif-elsif-else statement, 5 or more conditions.
- Covert the 5 or more decisions to a switch-case-case-case-case-otherwise.
- Make a markdown block before each code example
- Comment/establish a style of comments for your if-elseif and switch-case code blocks
- Finish lesson with De Morgan’s law
- Describe De Morgan’s law
- Illustrate De Morgan’s law
- Show some code running that shows understanding
- Resources, it is really time to show you can find resources beyond the Teacher
- Code/Code/Coding is everywhere, find something that helps
Week 2 - 8/30 Notes
- Java can create objects with..
- Scanner Class - inputs/outputs
- System Class - output to console using static method
System.out.printf() - Math Class - call a static method
Math.random()
- Other College Board Topics:
- 2D Array to store colors
- x –> color; y –> color code
- Control Structure - used to process a Menu
Front-end
- Fastpages is front-end
- Runs in browser
- HTML & CSS
- No server to run on
- GitHub Pages are also front-end
- Find a theme that works other than Minima on fastpages
- Challenge: take Liquid/JavaScript and see if you can build Mr. M’s schedule
- Do a time-box of your own schedule
Human Day 1
- must do for review (or else -0.25 to score)
- review score at top of review ticket
- link to fastpages
- tickets are with 4 person group
Week 1 - 8/23 Notes
- Python - weakly type language
-
Java - strongly type language
- In Java, you have to declare data types
- In Python it automatically changes data types
-
Java is OOP
- Primitive Data Types
- Boolean
- Character
- Integer
- Double/Float
- Long
- Short
- Non-Primitive: (classes)
- String
- Array
- etc.
-
Wrapper class - contains methods (functions)
- Opening notebook - vs code > apcsa repo > notebooks directory